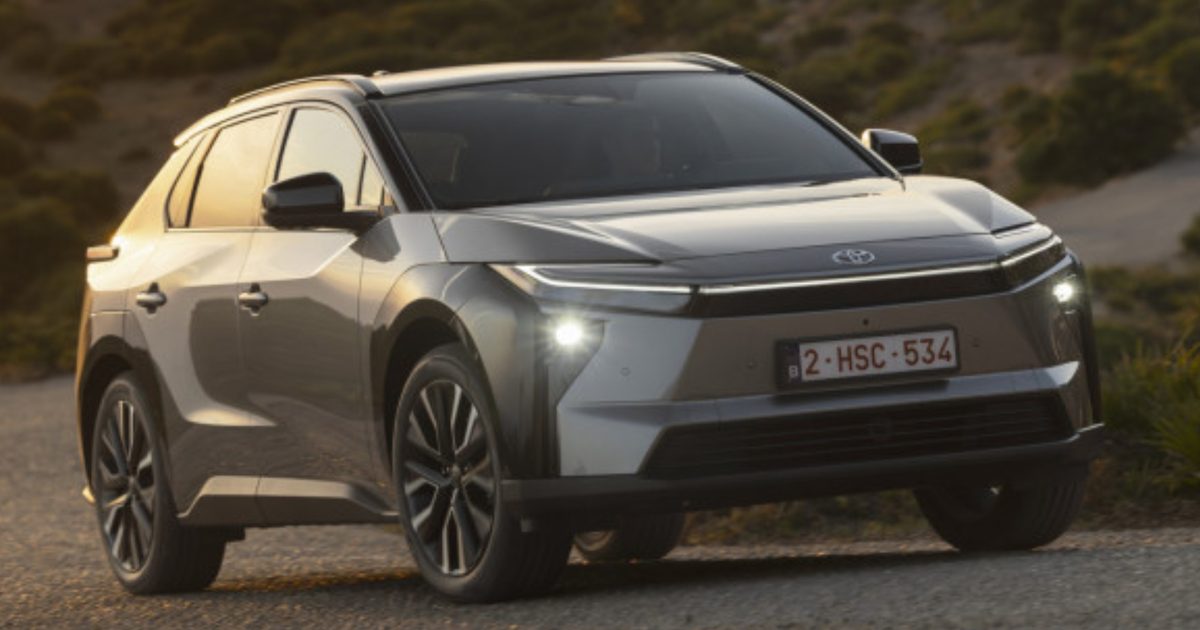
Toyota, along with the Chinese autonomous-driving firm Pony.ai, has announced that its first mass-produced robotaxi, based on the Toyota bZ4X, has rolled off the production line.
The project is a joint venture between Toyota Motor China, GAC Toyota, and Pony.ai, with themanufacturing handled by the latter two. Unlike prototypes that live their life on press stages, the robotaxis are headed for real-world service.
From prototype to production
The companies, as mentioned in the official press release, plan to build more than 1,000 Toyota bZ4X robotaxis this year, with gradual commercial deployment across China’s tier-one cities.
At the heart of the robotaxis is Pony.ai’s latest, seventh-generation autonomous driving system, which cuts the bill of materials for the self-driving kit by 70% (compared to the previous generation), while using 100% automotive-grade hardware. With this, the firm expects its total robotaxi fleet to exceed 3,000 vehicles by the end of 2026.
Inside, the Toyota bZ4X-based Pony.ai robotaxis offer features that should feel familiar to anyone who has used a modern ride-hailing app: Bluetooth-based automatic unlocking, voice interaction, online music, pre-trip climate control, and smoother braking and acceleration for enhanced comfort and reduced motion sickness.
Scaling fast, the Toyota way
The robotaix are built using the Toyota Production System and adhere to Toyota’s “QDR” principles, which stand for “Quality, Durability, and Reliability.” While Tesla and Waymo often grab attention with cutting-edge software, Toyota is leaning into scale, cost control, and manufacturing discipline.
“Together, these efforts demonstrate a clear pathway for autonomous driving technology to progress from limited-scale validation to large-scale mass production.”
Right now, the U.S. robotaxi landscape looks like a race where some runners already have a head start. Waymo, for instance, is doing extremely well in commercial deployment, operating around 2,500 fully autonomous robotaxis in multiple U.S. cities. Tesla is scaling its service out of Austin with a controlled, well-equipped fleet.
However, given that Toyota’s robotaxis are currently available only in China, they’re competing with local players like Baidu’s Apollo Go, WeRide, and AutoX.
Read the full article here