Creating, organizing, and sharing computation documents is essential in programming and data sciences. Most people turn to one of two popular tools — Google Colab and Jupyter Notebook — to help them manage their files.
SEE: Learn how to become a data scientist.
What is Google Colab?
Google Colab is a tool offered by Google Research that allows users to write and execute Python code in their web browsers. Colab is based on Jupyter open source and allows you to create and share hosted computation files in the cloud without downloading or installing anything.

What is Jupyter Notebook?
Jupyter is the original free, open-source, web-based interactive computing platform spun from the IPython Project; Jupyter Notebook is a web application that allows users to create and share computation documents.
1
Quickbase
Employees per Company Size
Micro (0-49), Small (50-249), Medium (250-999), Large (1,000-4,999), Enterprise (5,000+)
Small (50-249 Employees), Medium (250-999 Employees), Large (1,000-4,999 Employees), Enterprise (5,000+ Employees)
Small, Medium, Large, Enterprise
Features
Agile Development, Analytics / Reports, API, and more
Google Colab vs. Jupyter Notebook: Comparison table
| Software | ||
|---|---|---|
| Starting price | ||
| Free plan | ||
| Cloud based | ||
| File syncing | ||
| File sharing | ||
| Library install | ||
| File view without install |
Google Colab and Jupyter Notebook: Pricing
Google Colab and Jupyter Notebook are both free to use. Jupyter Notebook was released as an open-source tool under the liberal terms of the modified BSD license, making it 100% free to use.
Although Google Colab is also free, you may have to pay for advanced features as your computing needs increase. The following are the paid plans offered by Google Colab:
- Pay As You Go: For this plan, there are no fixed subscription fees; you only pay for what you use.
- Colab Pro: For $9.99 per month, you get 100 compute units, access to higher memory machines, and the ability to use a terminal with the connected virtual machine.
- Colab Pro+: For $49.99 monthly, you’ll get 500 compute units, faster GPUs, and background execution capability.
Feature comparison: Google Colab vs. Jupyter Notebook
Cloud-based
Google Colab’s major differentiator from Jupyter Notebook is that it’s cloud-based, and Jupyter isn’t. If you work in Google Collab, you don’t have to worry about downloading and installing anything to your hardware. It also means that you can rest easily knowing that your work will autosave and back up to the cloud without you having to do anything.
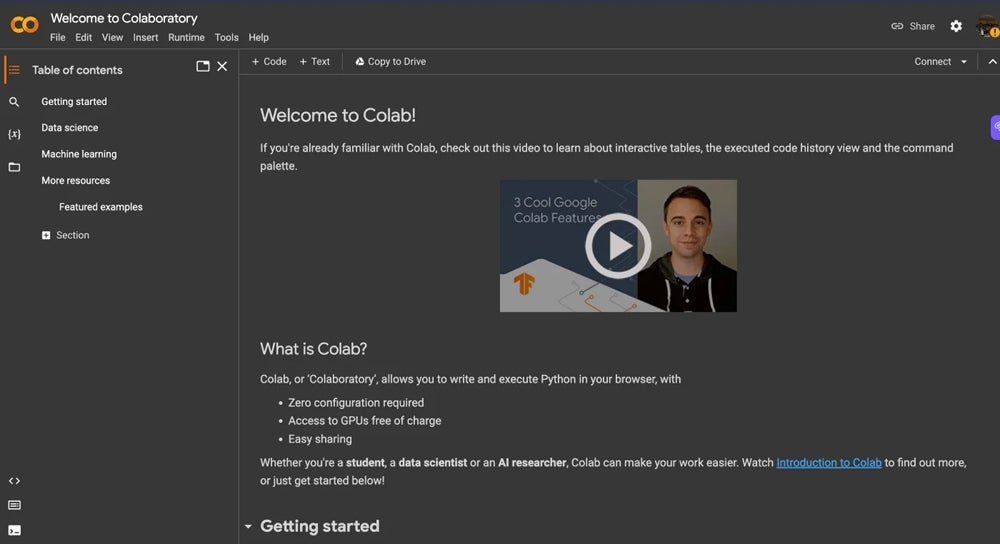
Google Colab is great if you need to work across multiple devices — such as one computer at home and one at work or a laptop and a tablet — because it syncs seamlessly across devices.
In contrast, Jupyter Notebook is run on your local machine, and files are saved to your hard disk. Jupyter offers an autosaving interval that you can change but doesn’t back up to a cloud. Therefore, if your machine is affected, you’re out of luck. Jupyter can’t sync or share your files across devices without a third-party file-sharing service like Dropbox or GitHub.
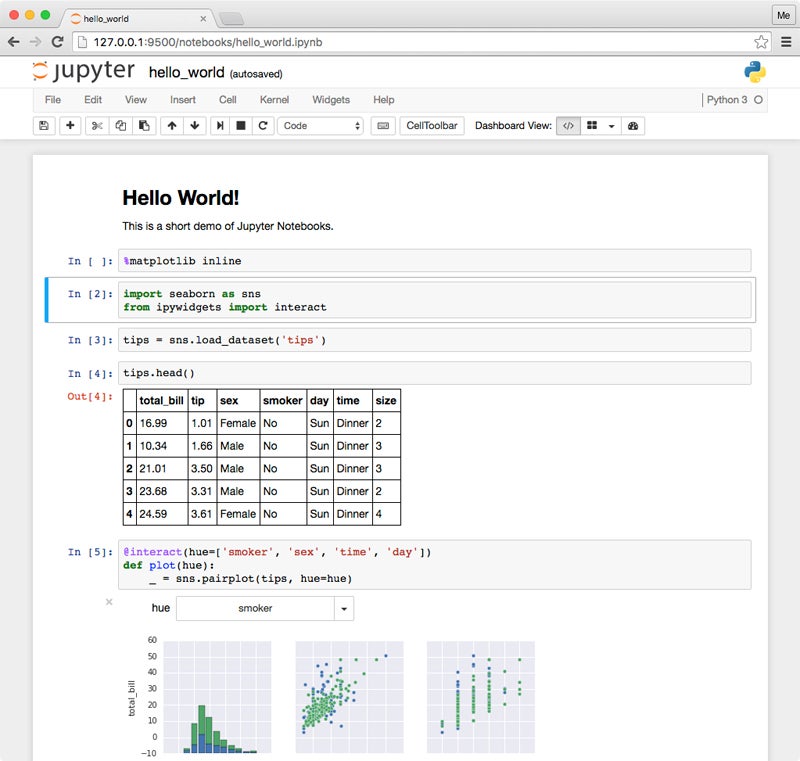
Collaboration
We couldn’t talk about Jupyter Notebook versus Google Colab without mentioning collaboration. As the name suggests, Google Colab is built to make it easy to share your notebooks with anyone — even if they’re not a data scientist. Other people can view your notebook without downloading any software — a big advantage if you regularly work with nontechies who need to access the files.
Conversely, anyone else must install Jupyter Notebook on their device to share their notebooks. This won’t be a hindrance if you solely work with developers, data scientists, and other tech people who will already have Jupyter installed. If you work on a more diverse team, then you might want to consider Google Colab because sharing files is easier.
Library install
Since Google Colab is cloud-based, the tool comes preinstalled with various libraries. This means that you don’t have to separate precious disk space or time to download the libraries manually. The free version also comes with a certain level of graphic processing units, memory, and run time, which can fluctuate. You can upgrade to one of the paid plans if additional capacity is needed. Google doesn’t disclose limits for any of its Colab plans due to the need for flexibility.
With Jupyter Notebook, you’ll need to install each library you’d like to use onto your device using pip or another package manager. You’ll also be limited by your computer’s available RAM, disk space, GPU, and CPU. Having the notebooks stored on your hardware is more secure than in a third-party cloud. Therefore, the manual library installation can be a plus for sensitive data.
R Scripts
Both Google Colab and Jupyter Notebook allow users to run R scripts, though they are primarily designed for Python. In Google Colab, users can now select to work with R by selecting it within the Runtime menu. For Jupyter Notebook, users must install an R kernel to work with R on their computer.
Google Colab pros and cons
Pros
- Straightforward interface that’s easy to navigate.
- Access GPU and TPU runtimes for free.
- Import compatible machine learning and data science projects from other sources.
- Automatic version control similar to Google Docs.
- Real-time collaboration capability.
- Integrates with other tools, including GitHub, Jupyter Notebook, BLACKBOX AI, Codeium, CodeSquire, Google Workspace, Neptune.ai, StrongDM, Google Drive and more.
Cons
- The free plan gives you limited resources.
- Some users reported issues with the speed of loading new databases and data frames that are present offline.
Jupyter Notebook pros and cons
Pros
- Modern, intuitive, and interactive user interface.
- Supports markdown language for documentation.
- Interactive interface makes it easy for users to share images, code, and text in one place.
- Supports multiple programming languages, including Python, R, and Julia.
Cons
- Some users reported that the software gets slow or crashes sometimes when working with large datasets or carrying out complex calculations.
- Some Jupyter Notebook users reported that tracking changes and collaborating using version control tools like Git can be complicated because notebooks are stored as JSON files.
Should your organization use Google Colab or Jupyter Notebook?
Both Jupyter Notebook and Google Colab may be the right choice in particular circumstances. Google Colab is an excellent choice for entry-level developers or nonprogrammers who want to start quickly without installing anything. It’s also a great idea for anyone who needs to share notebook files with people who won’t have the proper software installed on their devices.
Finally, Google Colab is a must for anyone looking to back up their work to the cloud and sync their notebooks across multiple devices — but the ease of cloud sharing means reduced data security.
Meanwhile, Jupyter is better for sensitive files that must be kept off the cloud. Installing the notebooks on your own hardware also means that you never have to worry about your GPU or runtimes getting throttled, which can happen sometimes on the Colab free accounts.
Review methodology
We reviewed both tools by gathering primary data from the vendors’ websites and documentation; this information includes features, pricing, and use cases. We also tested each solution to gain firsthand experience with its usability. To learn about users’ experience, we evaluated current and past users’ feedback from third-party review sites.
Ben Abbott updated this article in January 2024.
Read the full article here














